Describing motion with equations involves using the three simple equations for average speed average velocity and average acceleration and the more complicated equations known as kinematic equations. Motion can be described as.

Lesson 1 Position And Motion 1 Doc Name Pandaree Kongsaree Date Class Lesson Outline Lesson 1 Position And Motion A Describing Position 1 A N Is Course Hero
Motion is the process of changing position.

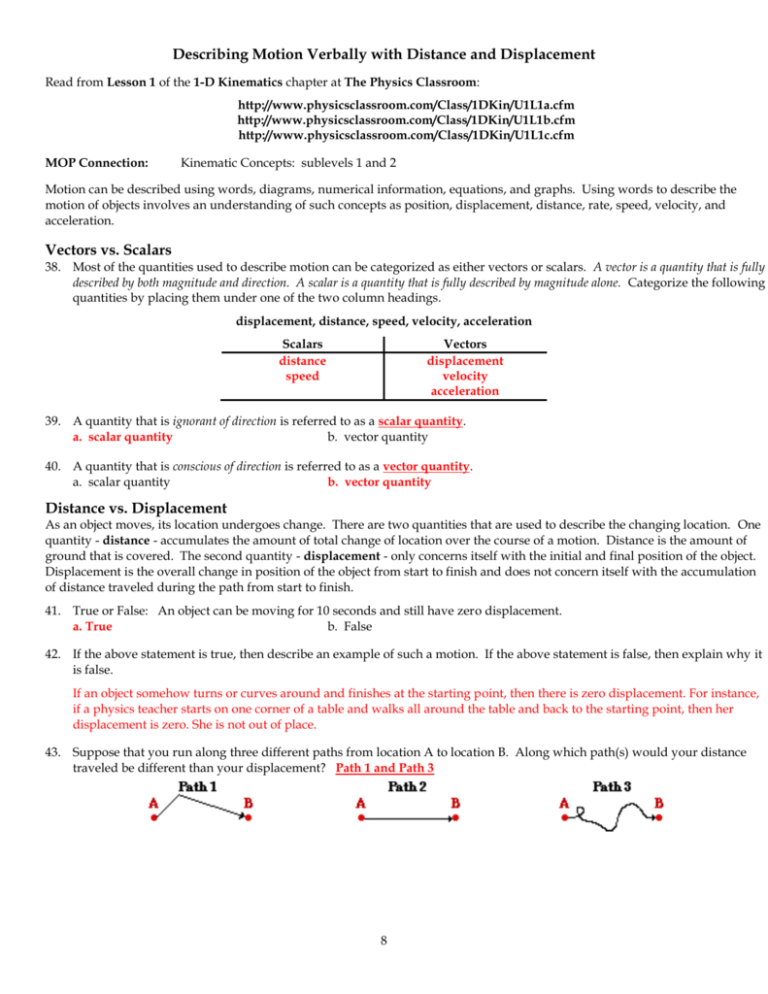
. You can measure how far something moves. An object is in motion if its position changes relative to reference point The distance an object moves and the objects displacement are not always the same. Most of the quantities used to describe motion can be categorized as either vectors or scalars.
Lesson 2 Speed is a measure of the distance an object travels per unit of time. The acceleration at any moment is equal to the slope of the velocity time graph at that moment in time Chapter 1. You need to compare motion to a reference point.
The motion of an object depends on the reference point that is chosen. 08 SCI Chapter 1 Lesson 1 - Position and Motion. Describing Changes in Position 1.
Use the diagram to answer each question. Compare and contrast the distance and displacement variables. 2nd Test - Chapter 1 Lesson 1 and 2 Science 6-2.
It is always described relative to a n reference point. Motion can be described using words diagrams numerical information equations and graphs. Speed can be calculated.
The starting point used to describe the motion or position of an object is called the reference point. Motion is the process of changing position. By definition if an object has a constant velocity then both the objects speed and its direction of motion are constant.
8th grade science test on chapter 8 review. Speed is determined by. The starting point used to describe the motion or position of an object is called the reference point.
If an objecti is in motion it changes position relative to its. Students should include a distance a direction and a reference point. I am 2 m to the right of the door.
Speed answer choices distance time time distance distance time Question 4 30 seconds Report an issue Q. Noting that the expression M approx - f _ o f _ mathrm e is no longer applicable because the object is so close use the thin- lens and magnification equations to find the angular magnification of this telescope. The object is stationary.
A place or object used for comparison to determine if another object is in motion is called a answer choices comparison point reference point point of view motion detector Question 3 30 seconds Report an issue Q. A accelerationB velocityC all of theseD speed 2. Some things move faster than others.
For example the motion of the mail truck in Figure 1 would be different if the reference point were a car moving along the street instead of a mailbox. Some of the worksheets for this concept are Lesson 1 describing motion with words Science grade 1 forces and motion Describing mo tion Answer key describing motion Lesson outline for teaching Big idea a push or a pull is a force that makes things move Forces and motion. Powered by Blogger Theme images by Radius Images.
Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Describing Motion Lesson 1. Up to 24 cash back 1. It is possible to move with regard to one reference point and stay motionless with regard to another reference point.
A inertia and weightB mass and. Can an object have negative speed. Describing Motion 15 School to Home.
An object is in motion when its distance from another object is. She records a negative displacement. Motion occurs when an object changes its position relative to a reference point.
Up to 24 cash back describe the motion of objects involves an understanding of such concepts as position displacement distance rate speed velocity and acceleration. Ricardo and Joe live in houses on the same street as shown in the diagram. Motion in the reference direction.
What You Learned 1. Olivia is doing a motion experiment with a car on a track. Describing Motion - Lesson 1.
Describing Motion Answer Key Answer Key Describing Motion Lesson 1 Before You Read 1. Agree Read to Learn 1. Describing Motion with Words Distance and Displacement Distance and displacement are two quantities which may seem to mean the same thing yet have distinctly different definitions and meanings.
Up to 24 cash back Describing and Measuring Motion Answer Key Use Target Reading skills What You Know 1. The objective and eyepiece have focal lengths of 1500 and 0070 m respectively. Describe the motion of the car.
Physics Classroom Worksheets Key Unit 1 Describing Motion Worksheet Answer Key Fill Online Printable Fillable Blank Pdffiller 2 Answer Describing Lesson Motion. What is the difference between speed and velocity. The distance between your final position and your starting position is.
A timeB reference pointC speedD angle 3. The house is one block east and one block south of school is a set of directions in two. Describing and Measuring Motion How do you recognize motion.
Describing and Measuring Motion How do you recognize motion. Velocity speed and direction of an objects motion A. I am 3 km northeast of my friends house.
Direction of motion opposite the reference direction. Up to 24 cash back describe the motion of objects involves an understanding of such concepts as position displacement distance rate speed velocity and acceleration. Name Date Class LESSON 1 Position and Motion Key Concept How does the description of an objects position depend on a reference point.
Can it have negative velocity. It does not give any information about the direction and so does not measure velocity. Up to 24 cash back box.
The process of changing position. Distance is the total length of your path of motion. Most of the quantities used to describe motion can be categorized as either vectors or scalars.
A car speedometer measures only speed. Describing Motion Distinguish. The farther reference point has the longer arrow.
The distance between your final position and your starting position is displacement. Distanceis a scalar quantity which refers to how much ground an object has covered during its motion. A vector is a quantity that is fully described by both magnitude and direction.
Lesson 1 A reference point a direction and distance are needed to describe the position of an object. A moving object changes position. A complete description of motion includes an reference point your displacement.
The meter is the SI unit for distance. Distance is the total length of your path of motion. Average Speed distance traveled time Average.
Kinematics in One Dimension Answers to Questions 1. A vector is a quantity that is fully described by both magnitude and direction. Terms in this set 9.
Motion is the process of changing position.

Lesson 1 Position And Motion 1 Doc Name Pandaree Kongsaree Date Class Lesson Outline Lesson 1 Position And Motion A Describing Position 1 A N Is Course Hero

Chapter 2 Review Answers Docx Chapter 2 Review Answers Section 1 Reinforcement Describing Motion 1 E 2 B 3 A And C 4 D 5 Walking Home 6 You Can Course Hero

Chapter 2 Review Answers Docx Chapter 2 Review Answers Section 1 Reinforcement Describing Motion 1 E 2 B 3 A And C 4 D 5 Walking Home 6 You Can Course Hero
0 Comments